
Talent Acquisition is the process of identifying, attracting, selecting, on-boarding and retaining highly qualified individuals to achieve organizational goal. It is very much similar with Recruitment & Selection but in general there is a difference between talent acquisition and recruitment & selection.
Talent Acquisition is a more strategic process with a goal to find highly qualified employees whereas recruitment is the more operational task of filling vacancies. Talent acquisition includes strategic recruitment, employer branding, and much more.
In some companies Talent Acquisition is done through a specialized department generally known as Talent Acquisition Team whereas in many company talent acquisition is a function of an HR generalist.
Let’s get Talent Acquisition process from practical point of view.
A talent acquisition process typically consists of below steps.
Organizational Needs Analysis
Manpower Planning
Approval of MRF (Manpower Requisition Form)
Vacancy Intake
Determining Selection Process
Candidate Attraction & Sourcing
Candidate Selection
Background Verification
Negotiation
Job Offer
Onboarding
1. Organizational Needs Analysis: It is the foundation of Talent Acquisition. Every organization should have a clear Vision, Mission & Values as well as those needs to be converted into goal, functional competency & behavioral competency. If you don’t have goal, functional competency & behavioral competency then it’s the time to convert your vision into goal, mission into functional competency & values into behavioral competency.
2. Manpower Planning: Your organization should have an approved manpower planning in alignment with your business strategy. This manpower planning may be a detailed manpower planning or at least an organogram (must be updated every year) of each & every department. But manpower planning is a must & HR capping is a prerequisite of effective talent acquisition. Financial budget needs to be considered during manpower planning.
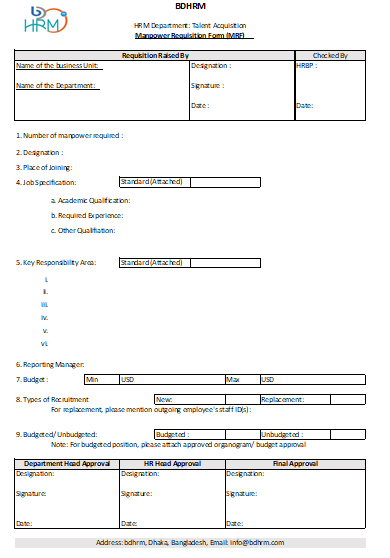
3. Approval of MRF: An approved Manpower Requisition Form (generally known as MRF) is a formal process of starting manpower hiring. A MRF may be a complex format in a HR management software or simply an approval on a specific format in Mail/ Hard copy. A sample MRF is shown here (you are required to customize basis your need):
4. Vacancy Intake: Standard organization should have a well-defined Job Description with Job Specification and Competency Framework (i.e. functional & behavioral competency library) for every role. If your organization don’t have, then conduct a job analysis and collect all the relevant information to make a good hire. This includes:
- The job description, including all required skills, competencies, and daily activities for the job
- The person specification, which is a description of the qualifications, skills, experience, knowledge and other selection criteria for a candidate. This includes the mandatory requirement & optional requirement extra-ordinary candidate.
- The competency framework (i.e. functional & behavioral competency library), which lists the required minimum and required competencies for the job.
5. Determining Selection Process: Based on the vacancy intake, the selection criteria and method are determined. There are many possible selection methods, including a written test, general interview, Assessment Center, Group Discussion, Presentation, Competency based interview, behavioral event interview, Work sample test and Psychometric Analysis (e.g. MBTI, DISC etc.) etc. or even a detailed Project Submission. You need to choose the best selection method or the best combination of selection method for different role.
6. Candidate Attraction & Sourcing: It is the most visible part of Talent Acquisition. There are various ways of attracting candidate like Internal Job Posting, Company Websie Job Posting, and Triggering to Registered candidates to apply for job, External Job Posting (e.g. Job Site Posting, Social Media Posting, Newspaper advertisement etc.), Campus Program etc.
Below are some important source of Candidates:
Internal Sources:
- Previous Applicants
- Present Employees
- Previous Employee
- Waiting List
- Employee Referral
External Sources
- Advertisements
- Campus Recruitment
- Job Fairs
- Social Media
- Employee Exchange
- Employee Leasing
- Walk in Interview
- Placement Agencies
- Acquisition & Merger
- Outsourcing
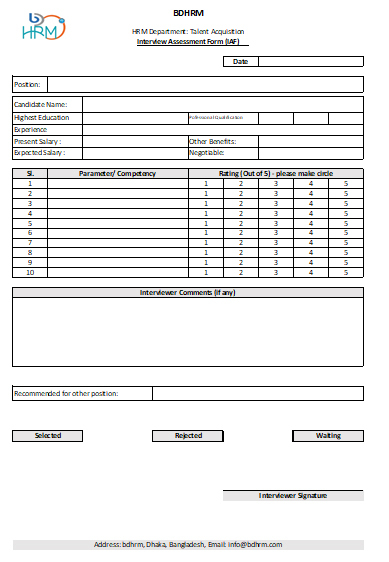
7. Candidate Selection: Once candidate applied, selection method are started. It starts with shortlisting the best candidates who fit with the job role. It is suggested to conduct a telephonic interview to avoid less matched candidate in final pool. Then different types of selection test needs to be done to select best fit candidate for the role as per organizational policy. It is recommended to conduct an Interview with the candidate with other required test. A sample interview assessment form is given for your consideration (you may make a customaries one for your organization).
Some Organization may do medical check-up also after final selection.
A sample Interview assessment form is shown below:
8. Negotiation: Negotiation may be required to fix the Salary of Selected candidate. Generally organizations should have fixed compensation package for a fresher and negotiation is required during hiring of experienced professional only. Salary may be negotiated but every organization should have a fixed benefit. Some organization might consider last organizations package to fix salary fitment.
9. Background Verification: Once candidate selection is done, it is the time of conducting background verification. Here, candidate educational qualification, professional certification, employment history, residence history, nationality, criminal record (some country may not allow), credit report (some country may not allow) is verified. Organization needs to develop suitable background verification policy for effective, time bounded & cost-efficient hiring.
10. Job Offer: Once everything is done, now it’s time to offer the job. Post job offer candidate needs to accept the offer. Some, candidate may reject the Job Offer, however offer acceptance rate may be an important HR metric.
Considering Offer acceptance metric, you can issue a Conditional Offer Letter and background verification can be done post acceptance of conditional offer letter.
11. Onboarding: Next step is onboarding the selected candidate & it plays an important role for employee retention. A great start can results a great future leader. Organization can make different onboarding plan generally starts with an orientation program. 30-60-90 day plan (or even 180-365) can be developed to onboard candidate. It can be a good practice to share some documents which includes.
Once the candidate accept the job offer, s/he can be considered as a part of your organization. Hence, some documents e.g. some common policy, company mission-vision-values, Job Role KRA can be sent 7 days prior to the candidate so that s/he can take mental preparation for first day.
You can arrange an onboarding kit or arrange a lunch with Manager & teams for a great onboarding.
